Applications
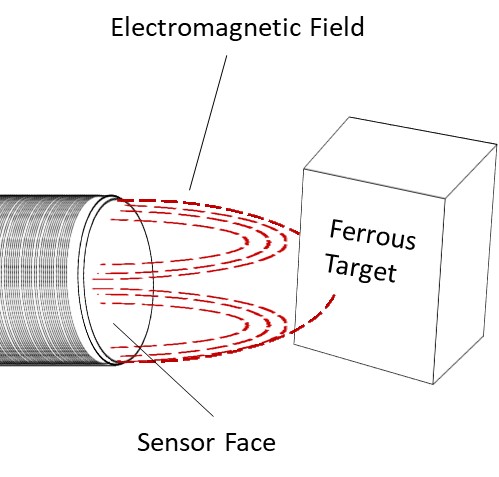
Magnetic proximity sensors including Hall effect and magneto-resistive sensors are used for detecting and positioning magnetic objects, angular positioning of parts in an assembly, and for controlling complex motor operations. Examples of applications of magnetic sensors include the positioning of robot arms and elevators, automotive parts and compassing. The durable nature of magnetic sensors and their ability to detect through a non-magnetic container make them suitable for usage within harsh and complex environments such as aerospace applications.
Advantages:
- Magnetic sensors can reduce cost and complexity for moving parts as one sensor can be matched to multiple magnets corresponding to different positions. An example would be in an elevator where a single sensor in the elevator responds to magnets positioned at each floor
- Long detection range
- Can detect through non-magnetic materials, e.g. plastic walls and pipes
- Typically low-maintenance and robust
- Broad operating temperature range
- Can be sealed in non-metallic containers for protection without impacting sensing performance, making magnetic sensors a good choice for harsh environments and aerospace applications
Limitations:
- Magnetic sensors will not detect non-magnetic objects and are therefore unsuitable for many counting and routing applications
- Cannot measure physical properties of the detected objects; only presence, absence or position
- For counting, fill-level, routing and quality control applications, consider capacitive sensors, photoelectric sensors or ultrasonic sensors
How helpful was this article? Click a star to rate.
[1 votes so far. Average rating of 5]







