Applications
Capacitive proximity sensors can be used in a wide variety of applications due to their ability to detect numerous types of materials. Some common examples would include material feeding applications such as hoppers, or detecting the level of liquid in a container. Its flexibility combined with its durability and resistance to outside interference makes it a common choice in many manufacturing environments, including food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, automotive and other machinery manufacturing. Other common examples would be detecting whether liquid is currently flowing through a pipe, or notifying a user that the ink level in an industrial printer was running low.

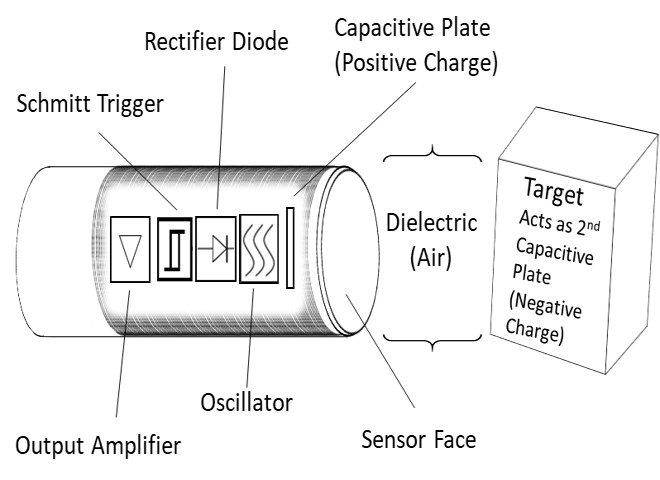
Advantages:
- Able to detect a wide range of materials including metal and non-metal as well as liquids
- Generally not susceptible to outside interference including electromagnetic, dirty environments or other contaminants
- Capable of withstanding harsh environments including industrial applications and washdown
- Generally easy to install and maintain
- Able to withstand a high number of cycles for a longer lifespan
- High switching rates to support faster cycle times
Limitations:
- Not well suited for low density materials
- Has one of the shortest ranges of all proximity sensors, usually less than 30 mm
- Can only detect the presence of an object, but not the shape, color or orientation
How helpful was this article? Click a star to rate.
[4 votes so far. Average rating of 4.5]